INTRODUCTION:
3D printing is a revolutionary technology that is going to change the way goods are manufactured. This technology is permeating every walk of life and every industry from medicine to architecture to manufacturing. Many countries across the world are investing heavily into this technology. Given the pace at which this technology is advancing, this shall soon become a common place a common household item.
What is 3D Printing?
3D printing or additive manufacturing is a process of making three dimensional solid objects from a digital file. The creation of a 3D printed object is achieved using additive processes. In an additive process, an object is created by laying down successive layers of material until the object is created. 3D Printing is the opposite of subtractive manufacturing in which we can remove material to create an object.
It has the potential to democratize the production of goods, from food to medical supplies. In the future, 3D printing machines could make their way into homes, businesses, disaster sites, and even outer space. 3D Printing technology was already being used by both small scale industries as well as large scale industries. As the need of 3D printers is growing for prototyping, modeling or low volume manufacturing requirements. 3Dprinters are offering very short lead times a wide range of materials at a low cost. A big chunk of people depends upon 3D printers and 3D Printing Services.
3D PRINTING TECHNOLOGIES:
The following are the technologies used in 3D Printing.
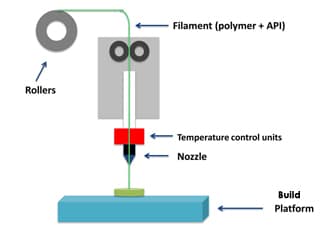
The process works by melting plastic filament that is deposited, via a heated extruder, a layer at a time, onto a build platform according to the 3D data supplied to the printer. Each layer hardens as it is deposited and bonds to the previous layer. The FDM/FFF processes require support structures for any applications with overhanging geometries.
Materials: ABS, Flexible, Nylon, PET, Wood, PLA, PC, HIPS
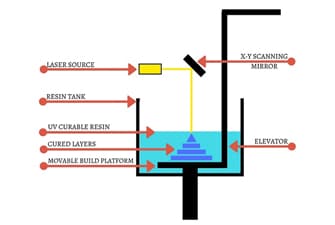
SLA is a laser-based process that works with photopolymer resins that react with the laser and cure to form a solid in a very precise way. A laser beam is directed in the X-Y axes across the surface of the resin according to the 3D data supplied to the machine (the .stl file), whereby the resin hardens precisely where the laser hits the surface.
Materials: Acura 25, Acura 60, Visijet tough, Visije clear, Visijet white
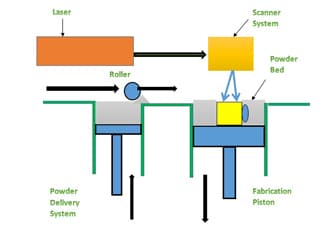
Laser sintering refers to a laser based 3D printing process thatworks with powdered materials. During SLS, tiny particles of plastic, ceramic or glass are fused together by heat from a high-power laser to form a solid, three-dimensional object.
Materials: PA Nylon (for regular applications), Glass filled Nylon (for higher strength applications)
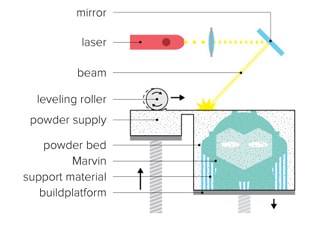
The DMLS machine begins sintering each layer—first the support structures to the base plate, then the part itself—with a laser aimed onto a bed of metallic powder. After a cross-section layer of powder is micro-welded, the build platform shifts down and a recoater blade moves across the platform to deposit the next layer of powder into an inert build chamber. The process is repeated layer by layer until the build is complete.
Materials: Maraging Steel MS1, Stainless Steel ss316, Cobalt Chrome cp1, Aluminium AlSi10Mg, Titanium ti64, Inconel (Nickel Alloy)
POLY JET PRINTING (PJP):
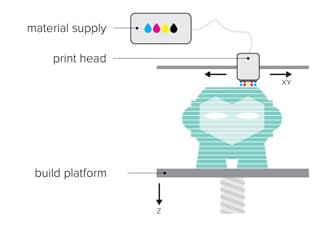
Polyjet process is a very precise 3D printing method, producing accurate parts with a very smooth finish. The nature of this product allows for the simultaneous deposition of a range of materials, which means that a single part can be produced from multiple materials with different characteristics and properties.
Materials: VeroWhite, Rigur, PolyjetFlex
COLOR JET PRINTING (CJP):
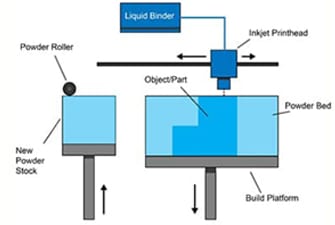
Can produce high-definition, full-color prototypes or earlystage concept models affordably, and within tight deadlines. As models are 3D-printed directly in color, ColorJet allows you to analyze color variations at an early stage without having to go for post-process painting. A cost effective solution for depicting complex objects in full color.
Materials: Sand stone powder
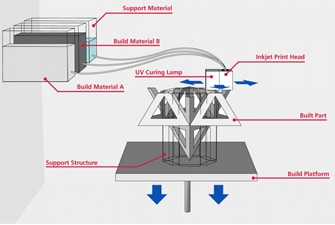
MJP is used to build parts, patterns and molds with fine feature detail to address a wide range of applications. The big benefit is that removing support material is virtually a hands-free operation and allows even the most delicate features and complex internal cavities to be thoroughly cleaned without damage.
Materials: VisiJet® M2 RCL Plastic Material, VisiJet® M2 EBK Elastomeric Material, VisiJet M2G – DUR ,VisiJet M2G – CL
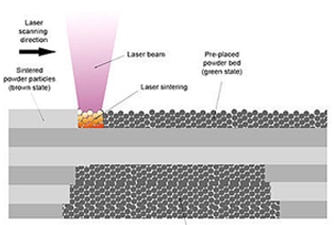
Multi Jet Fusion is a powder-based technology but does not use lasers. The powder bed is heated uniformly at the outset. A fusing agent is jetted where particles need to be selectively molten, and a detailing agent is jetted around the contours to improve part resolution. While lamps pass over the surface of the powder bed, the jetted material captures the heat and helps distribute it evenly.
Materials: PA12 (Nylon)
ADVANTAGES OF 3D PRINTING:
Faster Production:
3D Printing is faster than conventional manufacturing. From a prototype to a final product, 3D printing tests ideas and designs quickly.
Cost-Effectiveness:
Labour costs play a huge role in determining the amount of money to be spent in developing a prototype. Traditional manufacturing methods are require a lot of human labour. With 3D Printing, however, labour can be as little as one person issuing a print command.
Customization:
Not only does 3D Printing allow more design freedom, it also allows complete customization of designs.
Complexity and design freedom:
Designing geometrically complex shapes can be hard and expensive with traditional manufacturing technology but with 3D Printing you can create any complex designs more easily than traditional manufacturing methods. This gives designers a large amount of design freedom and enables the easy creation of very complex geometries.
Sustainability:
Subtractive manufacturing methods, such as CNC milling or turning, remove a significant amount of material from an initial block, resulting in high volumes of waste material.
Additive manufacturing methods generally only use the material needed to build a part. Most processes use raw materials that can be recycled and re-used in more than one builds. As a result, additive manufacturing process produces very little waste.
APPLICATIONS OF 3D PRINTING:
Medical & Health care:
3D printing has many functions in a variety of industries, however, in the medical field it has four main applications. This technology could be used to replace human organ transplants, speed up surgical procedures, produce cheaper versions of required surgical tools, and improve the lives of those reliant on prosthetic limbs.
Another application of 3D printing in the medical field is creating patient-specific organ replicas that surgeons can be used to practice on before performing complicated operations. This technique has been proven to speed up procedures and minimize trauma for patients.
Sterile surgical instruments, such as forceps, hemostats, scalpel handles and clamps, can be produced using 3D printers.
3D printing in the medical field can be used to produce prosthetic limbs that are customised to suit and fit the wearer. It is common for amputees to wait weeks or months to receive prosthetics through the traditional route; however, 3D printing significantly speeds up the process, as well as creating much cheaper products that offer patients the same functionality as traditionally manufactured prosthetics.
Manufacturing:
With a 3D printer on your desk you can easily create small parts and specialized tools yourself. It is far less complex than other machines, which means that you can produce more products in an efficient and simple way without the high costs. The 3D printers in our desk-series have a fast printing speed, a high accuracy and a low weight, making it easy to put on your desktop or move around.
The ability to use 3D printing to enhance business operations, reduce costs and improve efficiency is exactly why a 3D printer has become a popular solution. If you’re looking for a way to produce detailed and big objects our large volume 3D printers are an excellent choice. They have a much larger build size than most other industrial 3D printers and can print objects fast at a high resolution.
Industrial applications:
3D Printing can be used in the art, education, automotive and construction industries. 3D printing is used to manufacture moulds for making jewelry, and even the jewelry itself. It is becoming popular in the customisable gifts industry, with products such as personalized models of art and dolls etc.
- 3D printing is also being used by air forces to print spare parts for planes.
- 3D printing can also be used to make laptops and other computers and cases.
- 3D printing can be used to make miniatures, selfie models and etc.
Education:
Nowadays 3D Printing becomes more popular in education. It is becoming more and more important that students are not only exposed to 3D printing but also to have experience in it to benefit their future careers.
Apart from the above 3D Printing can be used in food industry, space, robotics etc.
Click here to know more about 3D Printers, 3D Printing services and it’s applications.
